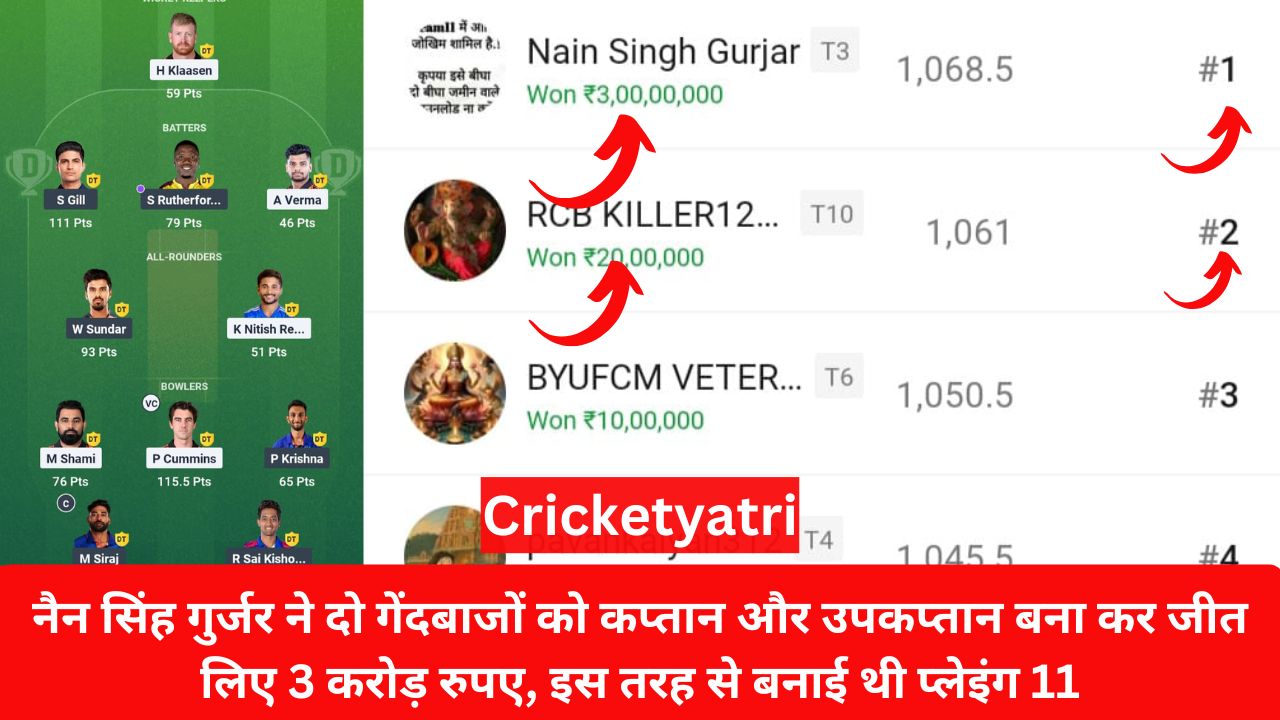
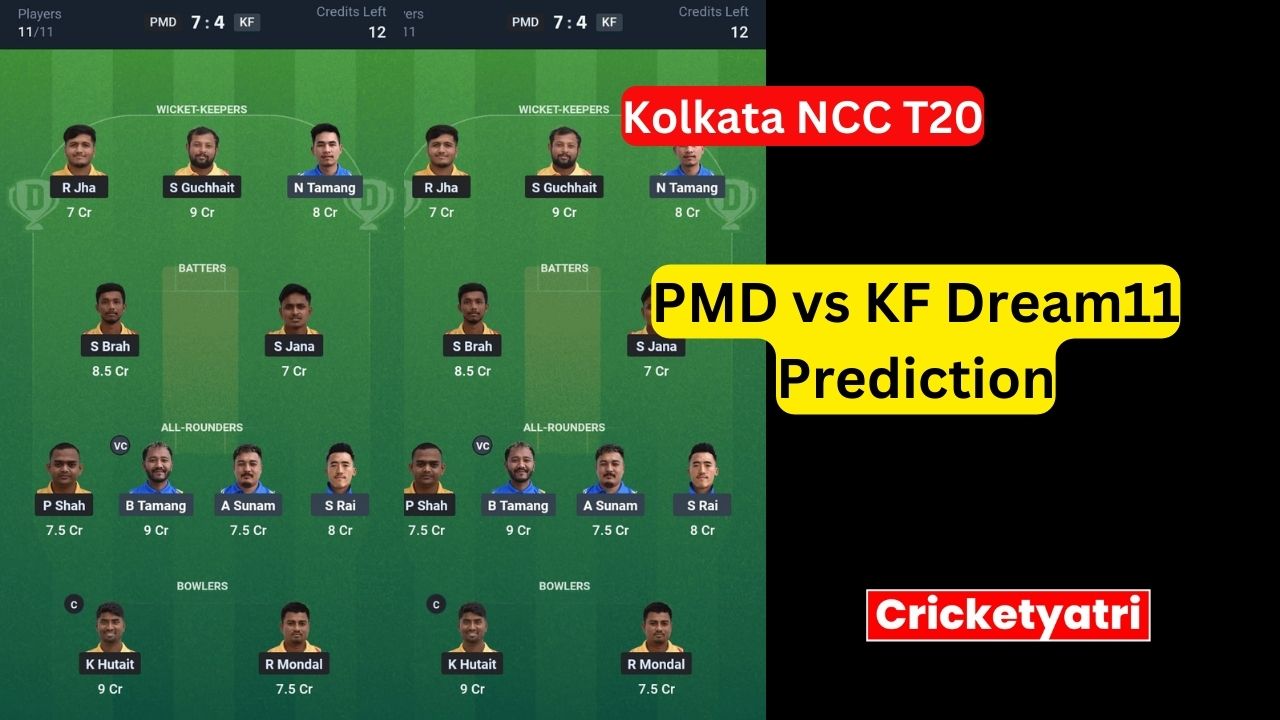
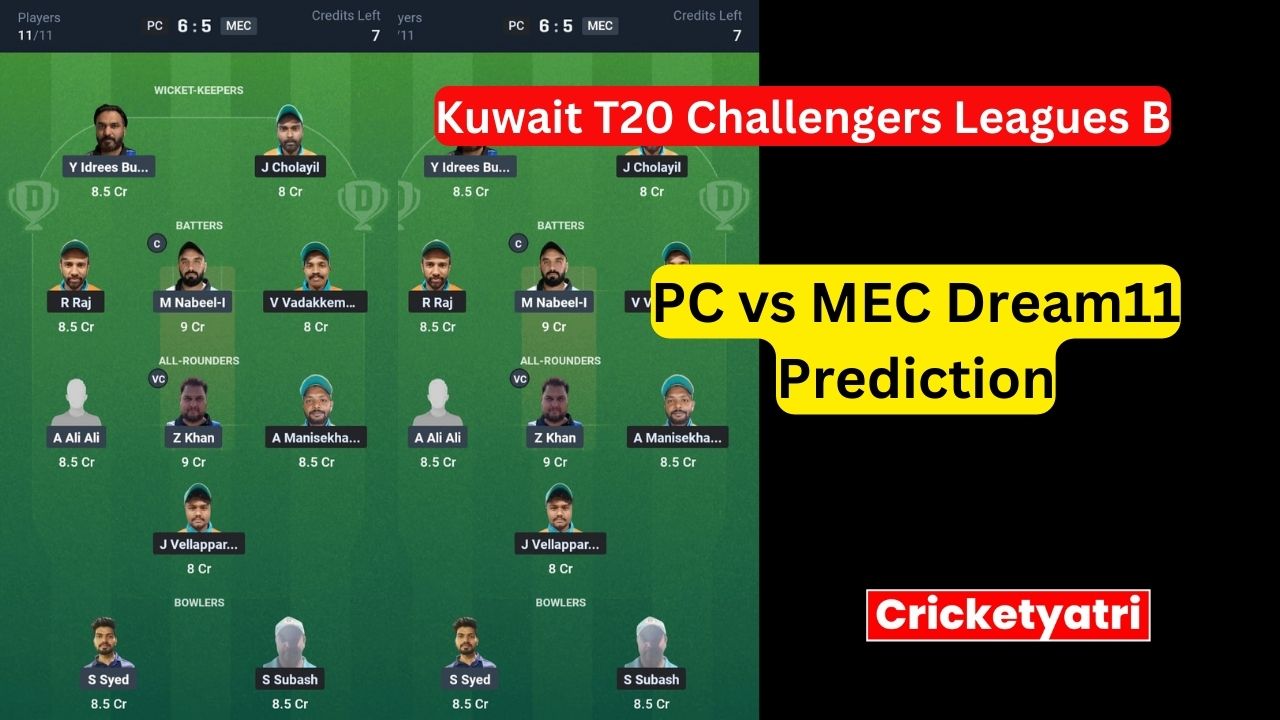
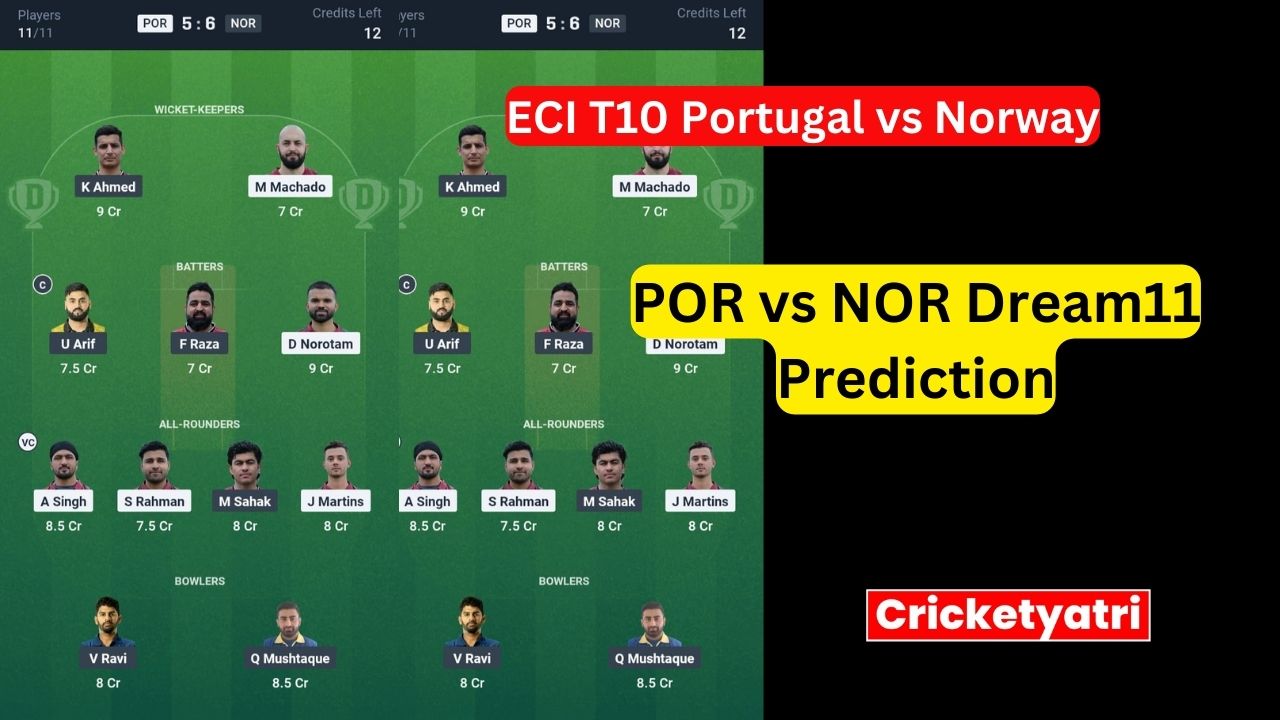
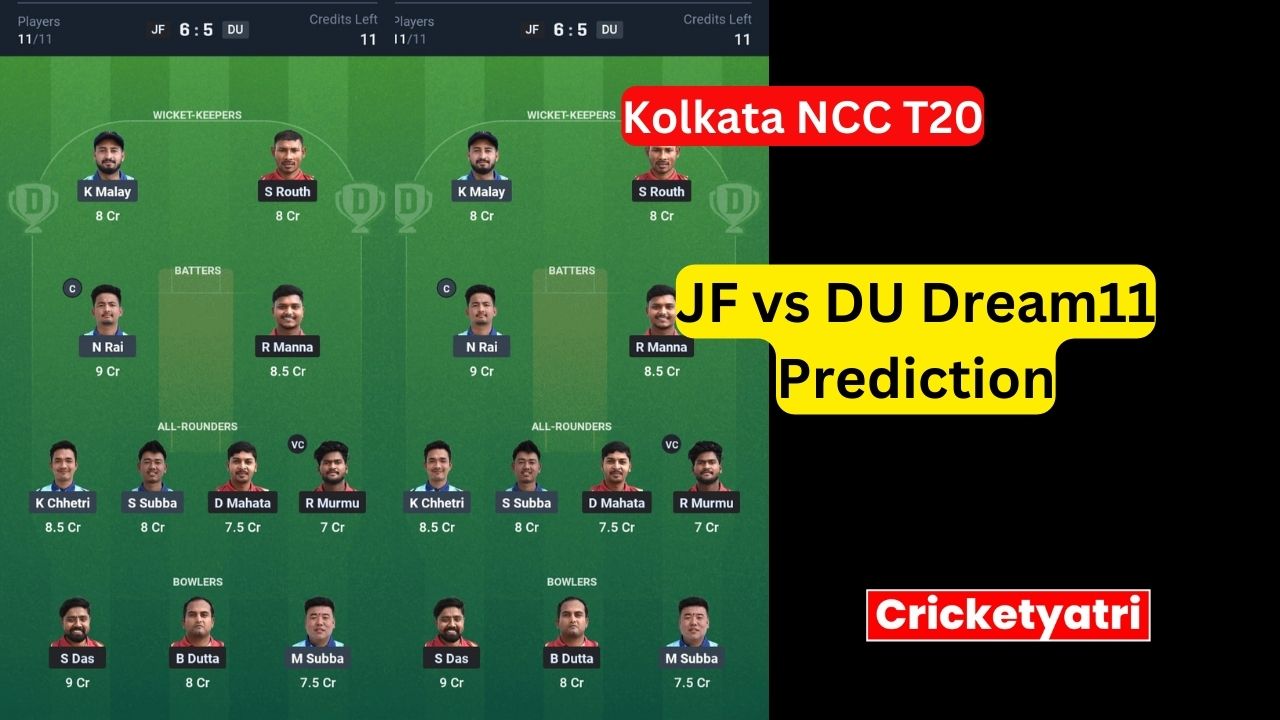
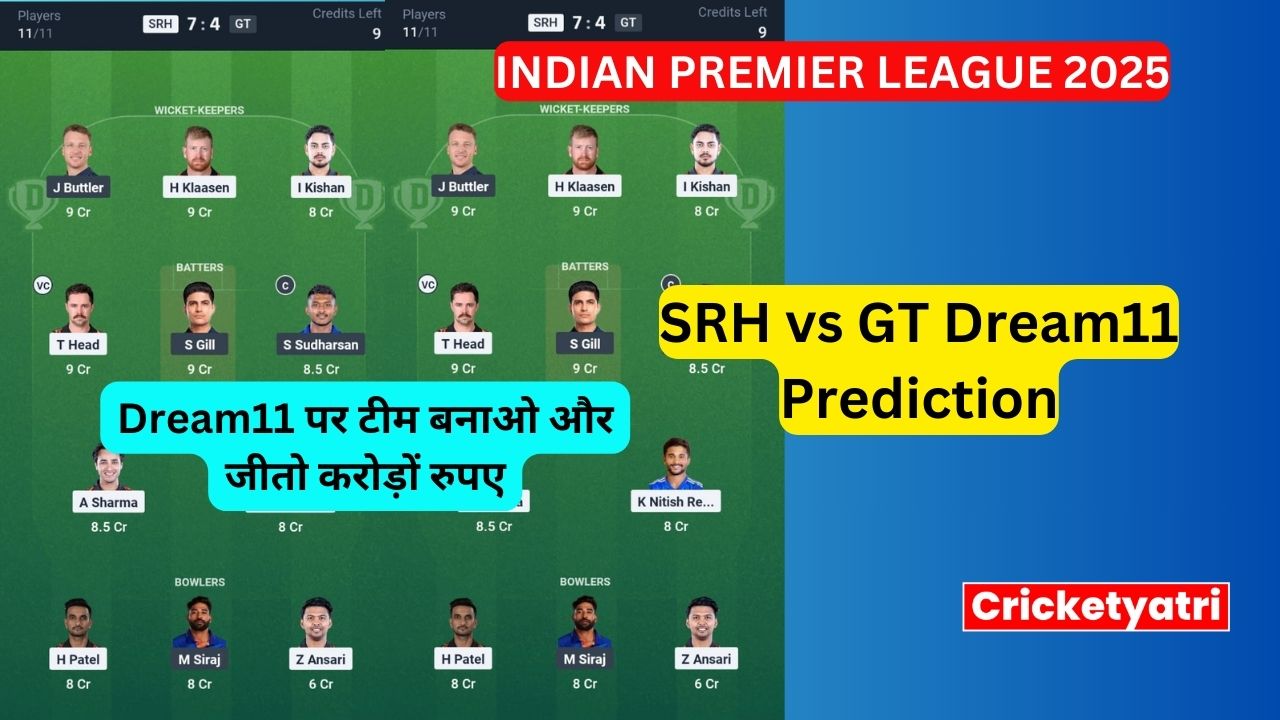
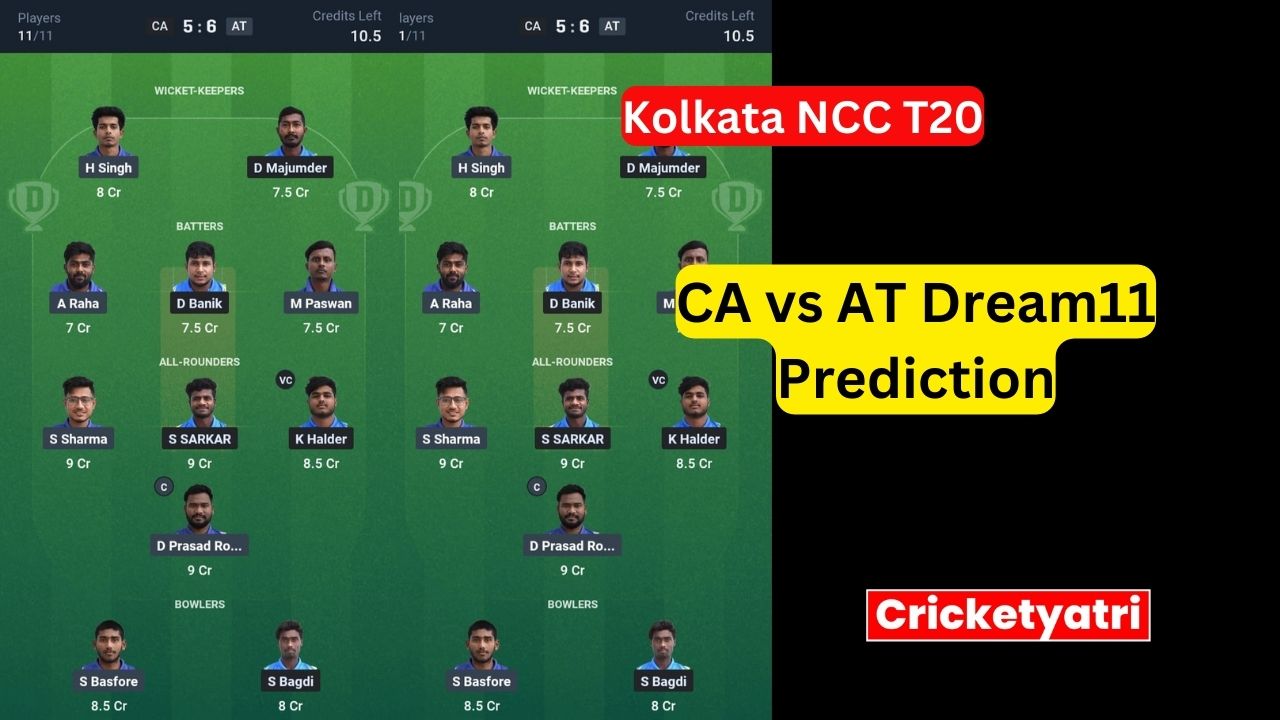
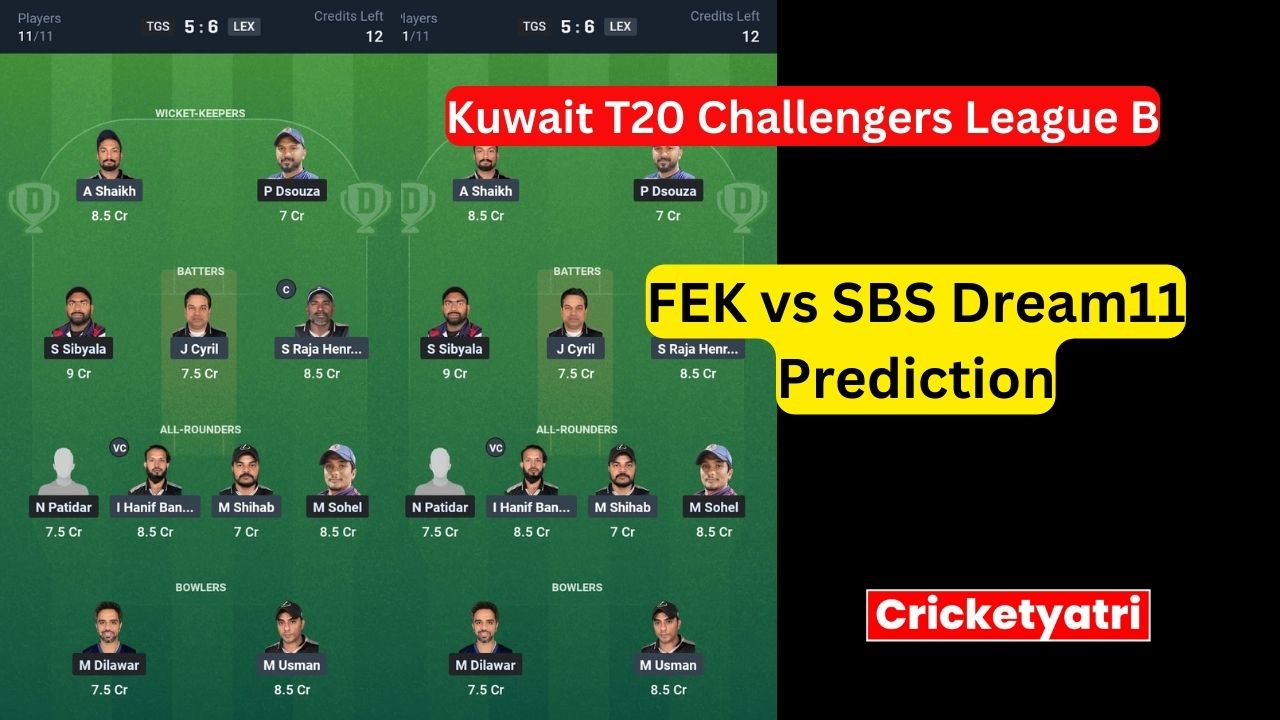
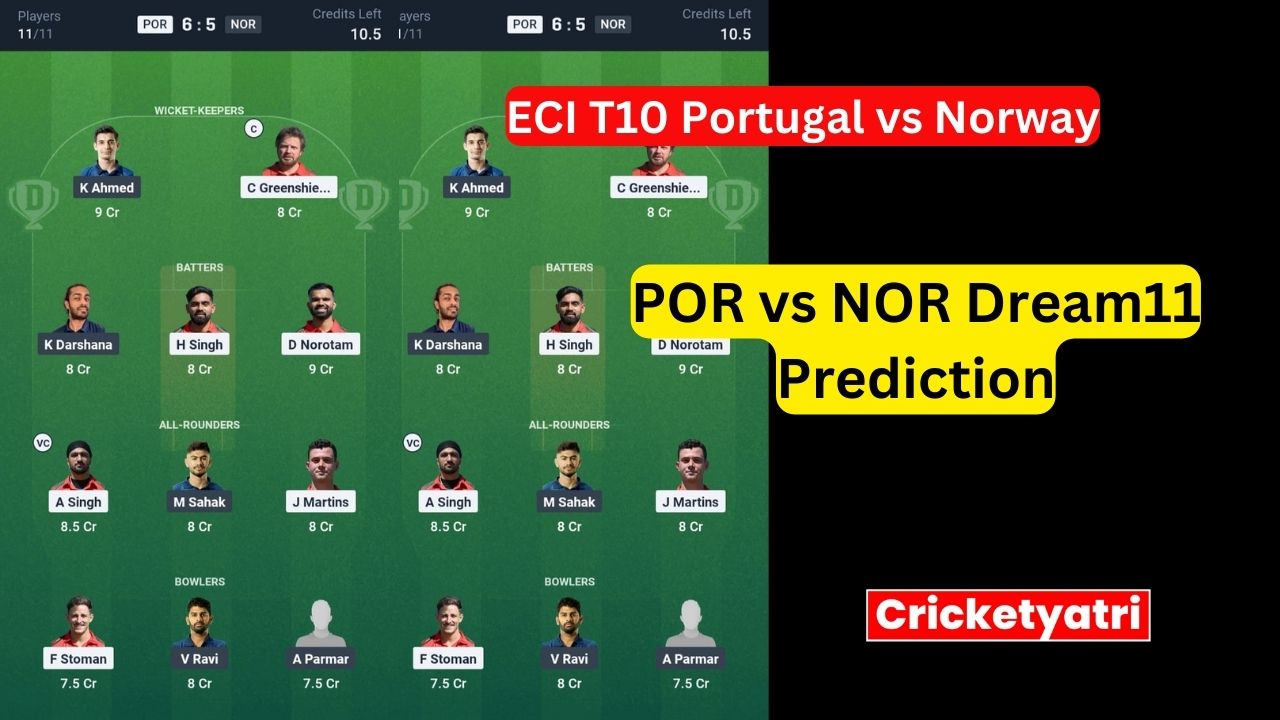
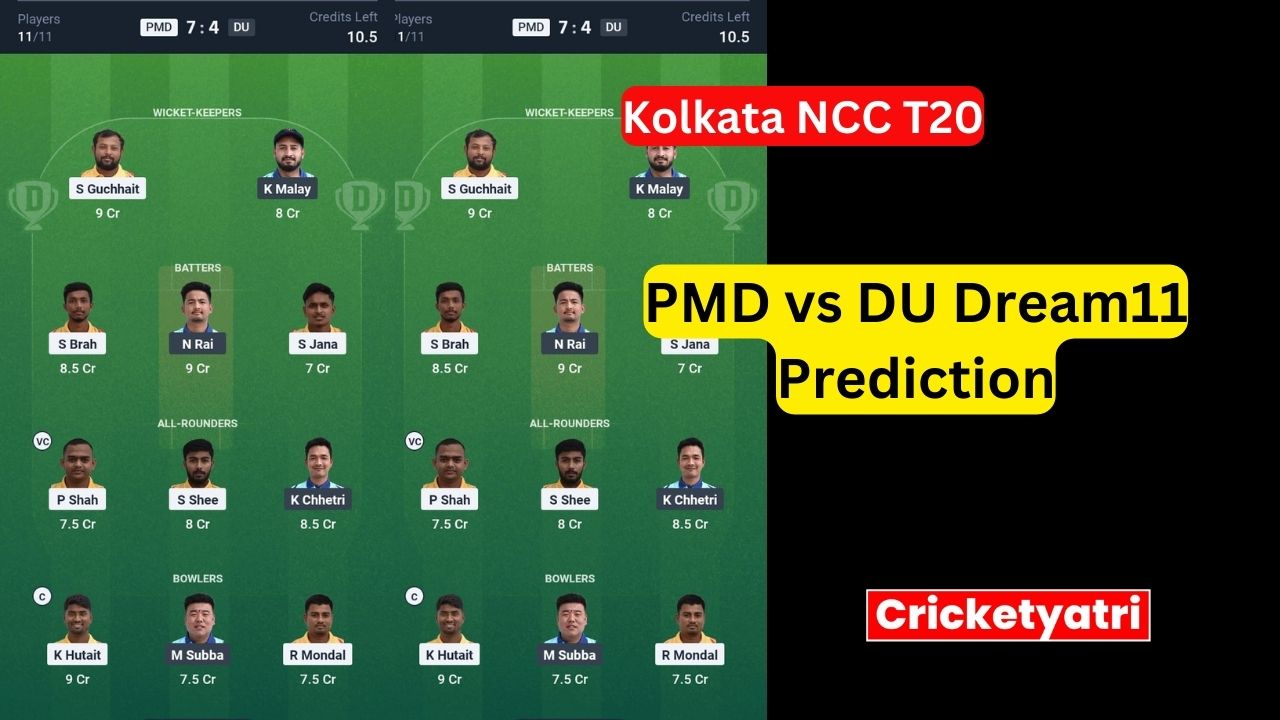
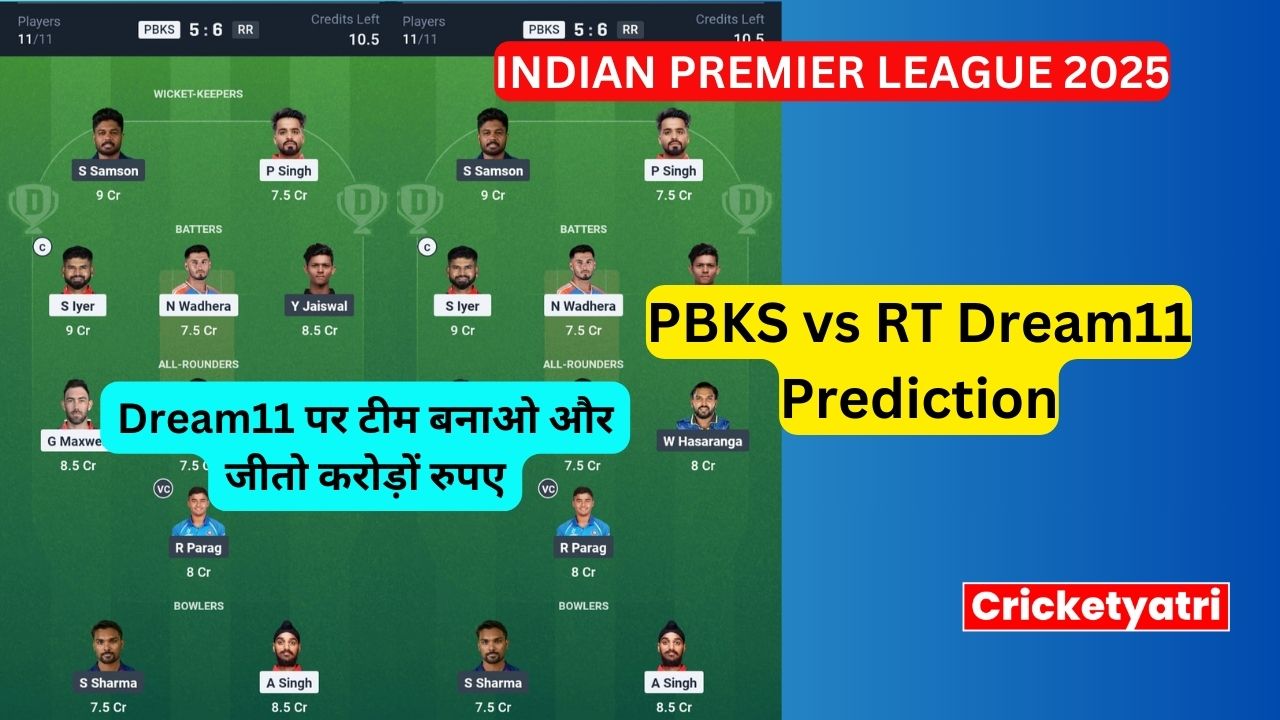
The main purpose of Cricketyatri is to update the cricket world. Through Cricketyatri users found the latest updates like – T20 World Cup, IPL 2023, Fantasy Cricket, Viral Cricket News, and many more. so please subscribe to this site for the latest updates.
Contact@cricketyatri.com
Other Pages
Trending Stories
© Cricketyatri (OPC) Private Limited | All rights reserved